Our modern lifestyle requires fundamentally new techniques to fortify the body against destabilizing external influences, in particular, soaring solar activity.
 The Aires Filter window is an optical filter with a matrix topology; it’s a technological development based on the principles of three-dimensional wave resonance. It is a three-dimensional wave analyzer that separates a stream of incoming electromagnetic fluctuations in the visible range into a series of phased, harmonic oscillations that coincide with the spatial Fourier spectrum.
The Aires Filter window is an optical filter with a matrix topology; it’s a technological development based on the principles of three-dimensional wave resonance. It is a three-dimensional wave analyzer that separates a stream of incoming electromagnetic fluctuations in the visible range into a series of phased, harmonic oscillations that coincide with the spatial Fourier spectrum.
The Aires Filter is a standard window which has had the Aires topological circuit applied to the interior surface of one of the window panes. As it interacts with the electromagnetic radiation passing through the circuit, including sunlight, it coherently transforms it, inducing a hologram that forms a spatial-temporal matrix of regularly alternating maxima and minima, capable of coherently counteracting the electromagnetic spikes that pass through it.
These windows are especially relevant in defending against the constantly growing solar activity that triggers changes in the planet’s electromagnetic field in an increasingly unpredictable manner as of late. Similar phenomena affect us all, negatively impacting how we feel and causing the development of extremely life-threatening diseases.
It is well known that fractals are the basis for the organization, operation, and management of hyperclustered systems, which includes humans. This means that the human body has properties of self-similarity at various levels of its system hierarchy, and it is evidence of the multi-dimensional “holographicness” of the body’s information system – the brain. As is known, a healthy body is distinguished by stable communication links, between its various functional systems and within each individual system and subsystem. A high level of synchronization of the body’s oscillating electromagnetic processes is a indication of the stability of these communication links.
The affect of the Aires Filter optical fractal-matrix filters on the behavior and synchronization of the brain’s bioelectric activity (BBA) has been investigated using electroencephalography. 27 test subjects were studied: 19 healthy persons and 8 patients with various neurological symptoms. EEGs from the patients’ medical histories manifest local (7 persons) or a combination of local and general paroxysmal activity without clinical implications.
The research was conducted in stages, with 5-10 minute intervals. In the first stage, a baseline EEG was recorded along with how it changed in response to hyperventilation of the lungs. In the second stage, an EEG was recorded while the subjects looked at a point light source (electric flashlight) for 10 minutes. In the third stage, an EEG was recorded while the subjects looked through the filters.
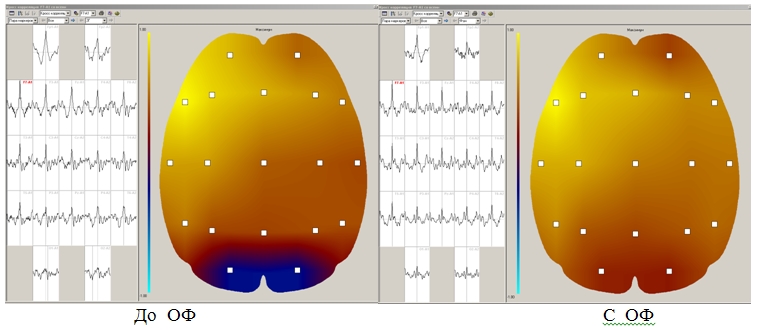
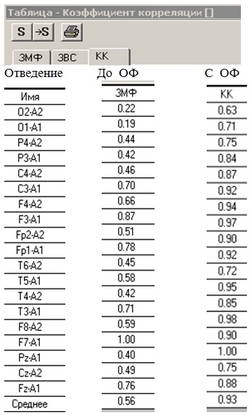
Change in the correlation coefficient (CC) when using Aires Filter optical filters. Positive CC values are shown in hues of red, while negative values are shown in hues of blue. The maximum positive CC value is 1; the maximum negative CC value is -1.
|
Degree of correlation for given CC values: Up to 0.3 – weak 0.3 – 0.5 – moderate 0.5 – 0.7 – significant 0.7 – 0.9 – high or close 0.9 – 1.0 – very high or very close |
Judging by the total correlation coefficient (CC) across all bands, the baseline EEG did not reveal substantial differences between the healthy subjects and the patients. During and after the hyperventilation (for 2 minutes), the EEGs of both groups showed a synchronization of EEG rhythms and an increase in CC (see the figure), most prominent in the left hemisphere. The elevated CC during hyperventilation was accompanied by an increase in the power spectrum in the delta-, theta-, and alpha bands, principally due to an increase in the amplitude of the waves without a shift of representations of individual frequency components in the cumulative EEG, which was caused by the activation of aerobic metabolism and, consequently, by a rise in the strength of sources of rhythmic activity and (or) their number.
Looking at a provisionally weak point light source led to an increase in the amplitude of the theta- and alpha activity on all leads and an increased CC, which was, however, not as prominent as what was observed with the hyperventilation.
The highest CC values were obtained when using the Aires Filter optical filters. A rise in CC was noted between all of the leads and across all bands, particularly the beta band. The peak frequencies were attenuated and the maxima were smoothed in each band. The growth of the strength of the alpha- and theta rhythms in the front leads was especially large. There were even high CC values measured between distant leads along the line between the forehead and the back of the neck, with higher CC values in the leads on the left hemisphere. The elevated CC was maintained with eyes open and closed, as well as after a 10-minute break. Opening the eyes caused only a partial depression of the alpha rhythm; during hyperventilation, the CC remained unchanged.
The patients exhibited both high CC as well as paroxysmal activity in the frontal-temporal leads on the left hemisphere, which persisted over the course of the next 2-3 hours. Given frequent, repeated use the filters (10 minutes; 3-4 times per day), the observed paroxysmal activity disappeared for 4-6 days while preserving the high CC values.
Interestingly, the test subjects reported that these changes in BBA were accompanied by a state of “pleasant relaxation”, “rest”, and “dissolution”. For the healthy test subjects, 10-minute sessions with the filters over the course of 6 days had an enduring positive effect on emotional vitality and relieved fatigue and irritability. Test subjects with an initially high synchronization in their EEG were observed to relax given sessions with the filters four times per week.
Thus, harmonic oscillations in the optical range, when projected onto the retina as light passes through Aires Filter matrix filters, elevate the coefficients of cross-correlation of the rhythm power spectrum in all EEG bands, between symmetric- and even distant leads. In keeping with the concept of the space-time interaction of nerve centers as one of the important principles in the organization of brain processes, in this case there is a global synchronization of brain processes and an increase in the brain’s activity as a system. This intense synchronization of BBA was caused by a reduction in the activity of the brain stem’s desynchronizing systems and a simultaneous increase in the activity of synchronizing systems in the mesodiencephalic level, particularly in the thalamic systems. The growth in the level of spatial synchronization of BBA correlates with a rise in blood circulation, including regional blood circulation, thereby creating the conditions necessary for increased brain cell metabolism. The brain’s increased systemic activity is associated with a state of relaxation with a reduction in behavioral activity. Based on this effect of the filters, Aires Filter can be recommended for use by persons with elevated levels of mental and emotional stress, as well as for use during work that strains the vision system.